![]() CUBA EXPLORE OIL FIELDS URGENTLY.
CUBA EXPLORE OIL FIELDS URGENTLY.
Oil stands out as one of the strategic points for the Cuban economy, and is among the sectors prioritised for the destination of foreign investment.
In addition, it is the essential basis of the electric power generated by the country.
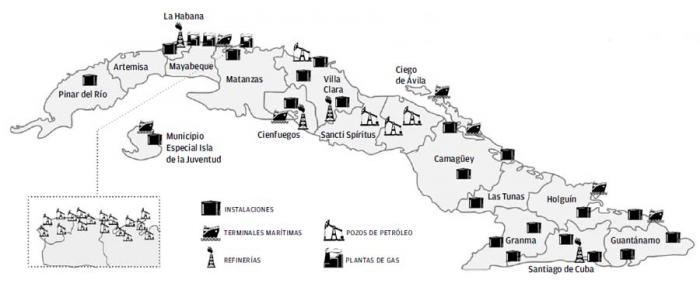
For this reason, Cuba-oil business group (Cupet) orients efforts immediate towards the search for new deposits, as more than 99 percent of the island’s oil production currently comes from the Northern strip of heavy crudes, an area that encompasses approximately 750 km² between Havana and Varadero, and which has been exploited for more than 40 years.
Cupet projections, moreover, are oriented towards raising the level of recovery of the existing deposits, through the introduction of enhanced recovery technologies; to achieve the sustained growth of domestic production and accelerate the exploration, evaluation and development of reserves in the exclusive economic zone.
Also, it aims to modernise existing refining capabilities and raise the quality of the national fuels to international standards.
EXPLORATION OF THE BASIN NORTH OF CUBA.
The geological service of the United States (USGS, by its acronym in English) recently evaluated the undiscovered resources of oil and gas in the North Basin of Cuba, in the Northwest of Cuba (fig. 1). The extension of the system of oil Total (SPT) compound of the Jurassic-Cretaceous defines the area assessed in this study (fig. 1). The demarcation of the composite SPT reflects the postulated extension of the migration of petroleum source rocks belonging to the times Jurassic and possibly Cretaceous, which have matured thermally. The evaluation of the basin North of Cuba is based on available information about the geological elements of the composite SPT defined in the basin, including source rocks for oil (maturation of source rocks, generation and migration of petroleum), rocks (sedimentology and Petrophysical properties) sites, and traps of oil (training and traps processing time). Through this geological structure, the USGS defined an SPT of the Jurassic-Cretaceous and three units of assessment (EU) within the SPT. In addition, quantitatively estimated the potential resources of oil and gas within the three EU ‘ as (table 1).
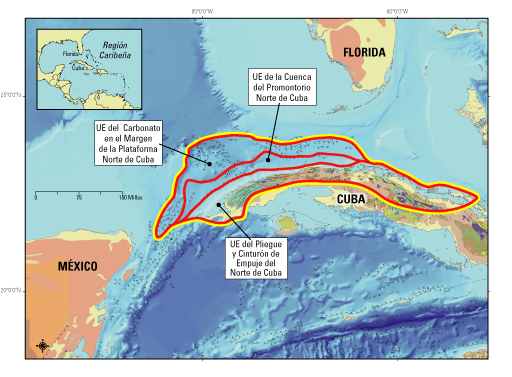
North Cuba Basin in the Northwest of Cuba. The demarcation (line yellow line) Total oil composed of Jurassic system – Cretaceous surrounds the three assessed units (EU) and defined in this study. The thin black lines represent failures on the ocean floor; Rod and ball show side moved down.”width =”512 “height =” 377 “class =”size-full wp-image-74974″/ > figure 1. North Cuba Basin in the Northwest of Cuba. The demarcation (line yellow line) Total oil composed of Jurassic system – Cretaceous surrounds the three assessed units (EU) and defined in this study. The lines black fine represent failures in the floor Ocean; Rod and ball are the moved side facing down.
The USGS evaluated resources potential of oil and gas conventional in the basin North of Cuba, excluding the growth of the book. The USGS estimated an average of 4.6 billion of barrels of oil (BBP), an average of 9.8 trillion of feet cubic (TPC) of gas natural (8.6 TPC of gas asociado-disuelto and 1.2 tpc of gas not associated), and an average total of 0.9 billion of barrels of liquids of gas natural in them three EU ‘ as (table 1). 4.6 average BBP, around 0.49 BBP is located in the EU of the fold and belt of thrust from the North of Cuba, about 3.2 BBP found in the EU of the basin of the promontory North of Cuba, and around 0.9 BBP has been estimated in the EU of carbonate in the margin of the platform in the North of Cuba (table 1). The total of non-associated gas (1.2 TPC; gas in gas fields) was evaluated in the EU of the promontory of the North Cuba Basin.
Agencies/Granma/Jesús Jank Curbelo/USGS/Excerpts/Internet Photos / Arnoldo Varona / TheCubanHistory.com
THE CUBAN HISTORY, HOLLYWOOD.
![]() CUBA EXPLORA YACIMIENTOS DE PETRÓLEO URGENTEMENTE.
CUBA EXPLORA YACIMIENTOS DE PETRÓLEO URGENTEMENTE.
El petróleo destaca como uno de los puntos estratégicos para la economía cubana, y figura entre los sectores priorizados para el destino de la inversión extranjera.
Además, es la base imprescindible de la energía eléctrica que genera el país.
Por ello, el Grupo Empresarial Cuba-Petróleo (Cupet) orienta sus esfuerzos inmediatos hacia la búsqueda de nuevos yacimientos, pues actualmente más del 99 % de la producción petrolera de la Isla proviene de la Franja Norte de Crudos Pesados, un área que abarca aproximadamente 750 km² entre La Habana y Varadero, y que ha sido explotada por más de 40 años.
Las proyecciones de Cupet, además, están orientadas hacia la elevación del nivel de recuperación de los yacimientos existentes, mediante la introducción de tecnologías de recuperación mejorada; a lograr el crecimiento sostenido de la producción nacional y a acelerar la exploración, evaluación y desarrollo de las reservas en la Zona Económica Exclusiva.
Asimismo, pretende modernizar las capacidades de refinación existentes y elevar la calidad de los combustibles nacionales a estándares internacionales.
EXPLORACIÓN DE LA CUENCA NORTE DE CUBA.
El Servicio Geológico de los EE.UU. (USGS, por sus siglas en inglés) evaluó recientemente los recursos no descubiertos de petróleo y gas en la Cuenca Norte de Cuba, en el noroeste de Cuba (fig. 1). La extensión del Sistema de Petróleo Total (SPT) Compuesto del Jurásico–Cretácico define el área evaluada en este estudio (fig. 1). La demarcación del SPT compuesto refleja la extensión postulada de la migración del petróleo de las rocas generadoras pertenecientes a los tiempos Jurásico y, posiblemente, Cretácico, que han madurado termalmente. La evaluación de la Cuenca Norte de Cuba está basada en información disponible sobre los elementos geológicos del SPT compuesto definido en la cuenca, incluyendo rocas generadoras de petróleo (maduración de rocas generadoras, generación y migración de petróleo), rocas en yacimientos (sedimentología y propiedades petrofísicas), y trampas de petróleo (formación y tiempo de transformación de trampas). Mediante esta estructura geológica, el USGS definió un SPT compuesto del Jurásico–Cretácico y tres Unidades de Evaluación (UE) dentro del SPT. Además, se estimaron cuantitativamente los recursos potenciales de petróleo y gas dentro de las tres UE’as (tabla 1).

Figura 1. Cuenca Norte de Cuba en el noroeste de Cuba. La demarcación (línea amarilla) del Sistema de Petróleo Total Compuesto del Jurásico–Cretácico circunda las tres unidades evaluadas (UE) y definidas en este estudio. Las líneas negras finas representan fallas en el suelo oceánico; la barra y pelota muestran la parte movido hacia abajo.
El USGS evaluó recursos potenciales de petróleo y gas convencionales en la Cuenca Norte de Cuba, excluyendo el crecimiento de la reserva. El USGS estimó un promedio de 4.6 billones de barriles de petróleo (BBP), un promedio de 9.8 trillones de pies cúbicos (TPC) de gas natural (8.6 TPC de gas asociado-disuelto y 1.2 tpc de gas no asociado), y un promedio total de 0.9 billón de barriles de líquidos de gas natural en las tres UE’as (tabla 1). Del promedio de 4.6 BBP, alrededor de 0.49 BBP se encuentra en la UE del Pliegue y Cinturón de Empuje del Norte de Cuba, unos 3.2 BBP se encuentran en la UE de la Cuenca del Promontorio Norte de Cuba, y alrededor de 0.9 BBP se ha estimado en la UE del Carbonato en el Margen de la Plataforma en el Norte de Cuba (tabla 1). El total de gas no asociado (1.2 TPC; gas en campos de gas) fue evaluado en la UE del Promontorio de la Cuenca Norte de Cuba.
Agencies/Granma/Jesús Jank Curbelo/USGS/Excerpts/Internet Photos/ Arnoldo Varona/ TheCubanHistory.com
THE CUBAN HISTORY, HOLLYWOOD.