NEW RUPESTRAL FINDINGS FOUND IN CUBA.
NEW RUPESTRAL FINDINGS FOUND IN CUBA.
In Cuba, 60% of the 304 rock art sites registered in Cuba until last year do not have patrimonial protection and 31% are outside the limits of the protected areas of the island, revealed the Cuban Speleological Society. showing thus the little attention that such important findings do not keep for the national authorities the importance that for the world they are of other generations within the country.
This happens in moments when new rock finds have been found during an exploration along the south coast of the Special Municipality of Isla de la Juventud, a group of speleologists from that territory, under the guidance of the engineer Arsenio Manuel Sánchez Pantoja, found inside a small cave of marine origin, located about 300 meters west of the town of Cocodrilo, a new site of Cuban rock art.
The site was discovered by a group of speleologists from the Isla de la Juventud Special Municipality during an exploration of the south coast of that territory.
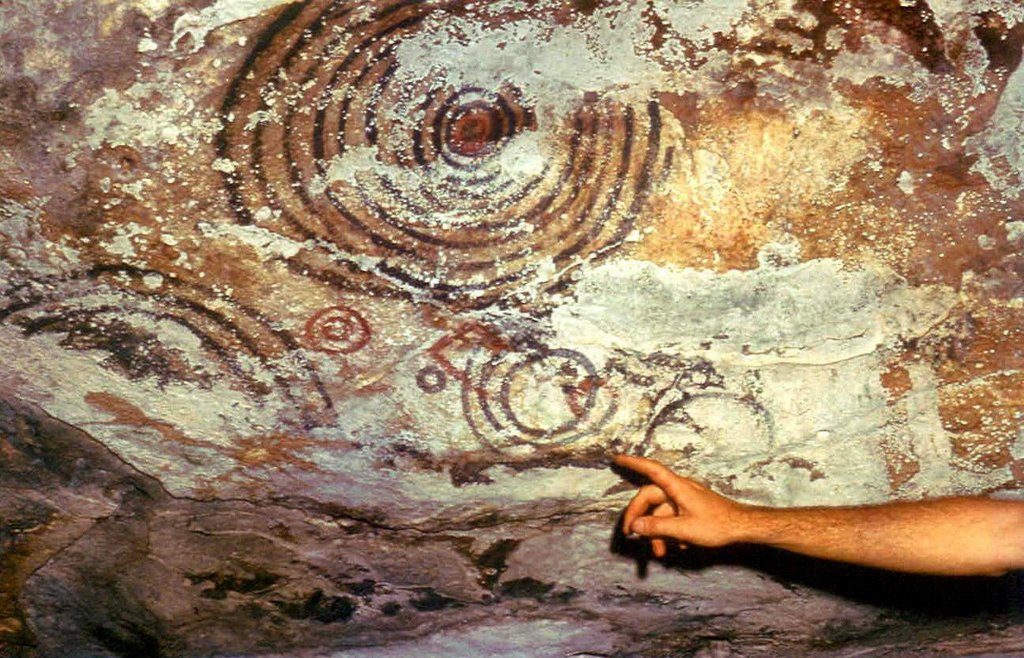
As reported by the Master of Science Divaldo Gutiérrez Calvache, president of the Speleological Society of Cuba and Coordinator of the Cuban Rock Art Research Group (Gciar), the finding consists of five unknown pictographs for the country’s rupestrology made in black, distributed in the walls of a gallery facing northeast.
The drawings, he stressed, are made up of series of six, five and four concentric circles, representations well extended in the rest of the rock art sites.
According to Gutiérrez Calvache, one of the peculiarities of the place that has been named Cueva del Criadero, because it is located under an old turtle hatchery, is that in the past only the subterranean grotto could be accessed through the sea, therefore, to make his paintings there, the pre-Columbian inhabitants had to enter by swimming or aboard boats.
With this, there are 14 rock art sites located in the Isla de la Juventud Special Municipality, while nationally the figure rises to 312, of which 198 have pictographs or paintings, 88 have petroglyphs or carvings and engravings on rocks, and 26 they present pictographs and petroglyphs.
On a global scale, rock art is considered one of the most valuable treasures of human culture and a source of forced study to pretend to know the way of life of our ancestors in its different edges. The foregoing establishes the urgency to move forward in the implementation of actions aimed at conserving and protecting this precious archaeological and cultural heritage of the Cuban nation.

Vista de la entrada a la Cueva del Criadero, donde se localizó el nuevo sitio de arte rupestre. foto: Ingeniero Arsenio Manuel Sánchez Pantoja
En Cuba el 60 % de los 304 sitios de arte rupestres registrados en Cuba hasta el año pasado no cuenta con protección patrimonial y el 31 % se encuentra fuera de los límites de las áreas protegidas de la isla, reveló la Sociedad Espeleológica de Cuba. mostrando así la poca atención que tan importantes hallazgos no guarden para las autoridades nacionales la importancia que para el mundo se encuentran de otras generaciones dentro del país.
Esto sucede en momentos que nuevos hallazgos rupestres han sido hallados durante una exploración por la costa sur del Municipio Especial Isla de la Juventud, un grupo de espeleólogos de ese territorio bajo la guía del ingeniero Arsenio Manuel Sánchez Pantoja, encontró en el interior de una pequeña gruta de origen marino, situada a unos 300 metros al oeste del poblado de Cocodrilo, un nuevo sitio de arte rupestre cubano.
El sitio fue descubierto un grupo de espeleólogos del Municipio Especial Isla de la Juventud durante una exploración por la costa sur de ese territorio.
Como informo el Máster en Ciencias Divaldo Gutiérrez Calvache, presidente de la Sociedad Espeleológica de Cuba y Coordinador del Grupo Cubano de investigaciones de Arte Rupestre (Gciar), el hallazgo consiste en cinco pictografías desconocidas para la rupestrología del país confeccionadas en color negro, distribuidas en las paredes de una galería orientada al nordeste.
Los dibujos, resaltó, están conformados por series de seis, cinco y cuatro círculos concéntricos, representaciones bien extendidas en el resto de los sitios rupestres pineros.
Según indicó Gutiérrez Calvache, una de las peculiaridades del lugar que ha sido nombrado Cueva del Criadero, por encontrarse debajo de un antiguo criadero de quelonios, radica en que en épocas pasadas solo podría accederse a la gruta subterránea a través del mar, por tanto, para realizar sus pinturas allí los habitantes precolombinos tuvieron que entrar nadando o a bordo de embarcaciones.
Con este suman 14 los sitios de arte rupestre localizados en el Municipio Especial Isla de la Juventud, mientras a nivel nacional la cifra asciende a 312, de los cuales 198 poseen pictografías o pinturas, 88 tienen petroglifos o tallas y grabados en rocas, y 26 presentan pictografías y petroglifos.
A escala mundial el arte rupestre es considerado uno de los tesoros más valiosos de la cultura humana y fuente de obligado estudio para pretender conocer la forma de vida de nuestros antepasados en sus diferentes aristas.
Lo anterior fundamenta la urgencia de avanzar en la implementación de las acciones encaminadas a conservar y proteger tan preciado patrimonio arqueológico y cultural de la nación cubana.
Agencies/Gramma/ Orfilio Peláez/ Internet Photos/ Arnoldo Varona/ TheCubanhistory.com
THE CUBAN HISTORY, HOLLYWOOD.