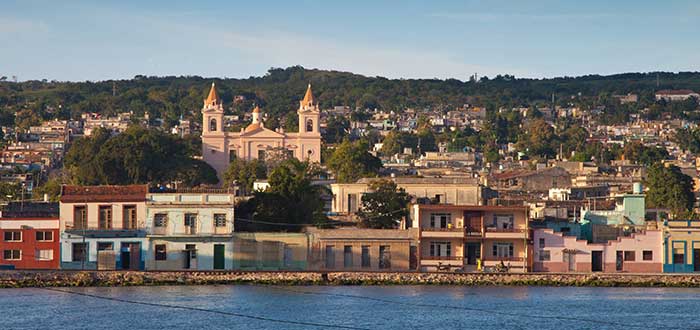 THE CUBANS: RACIAL COMPOSITION, DIASPORA, CULTURE, AND SYMBOLS.
THE CUBANS: RACIAL COMPOSITION, DIASPORA, CULTURE, AND SYMBOLS.
Cubans are the original people of Cuba. Most Cubans live in Cuba (11,193,470) in 2019, although there is also a large Cuban diaspora, especially in the United States where 1,343,960 Cubans lived in 2018, in Spain 151,423 (2019), and Mexico 22,604 (2016).
The provinces with the highest number of inhabitants in Cuba (2010) are Havana (2,135,498), Santiago de Cuba (1,047,963), Holguín (1,037,573), Granma (836,366), Villa Clara (800,335), and Camagüey (780 598). According to the National Statistics Office (ONE) at the end of December 31, 2010, the population was 11,241,11616 (5,628,996 men and 5,612,165 women).
RACIAL COMPOSITION.
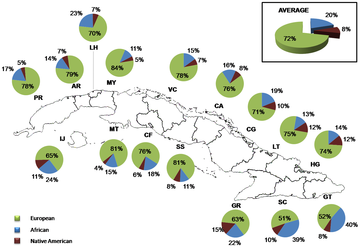
The racial composition in Cuba in 2002 was 7,271,926 whites, with blacks and mulattos being 1,126,894 and 2,658,675 respectively. The Chinese population in Cuba is mostly hired workers who arrived in the 19th century to build railways and work in the mines. After the Industrial Revolution, many of these workers stayed in Cuba because they could not pay for their passage back to China.
The ancestry of white Cubans (65.05%) comes mainly from Spanish. During the 18th, 19th, and first part of the 20th century, especially, large waves of the Canaries, Galicians, Asturians, and Catalans emigrated from Spain to Cuba. Other European nationalities who immigrated include: British, including Scots, Russians, Poles, Portuguese, Romanians, Italians, Greeks, French, Germans, and Irish. There is a small remnant of a Jewish community. There is also a significant ethnic influx of diverse peoples from the Middle East, especially Lebanese, Palestinians, Turks, and Syrians.
Afro-Cubans make up 10.08% to 23.84% of the population. Its origins are mainly Congo, people from Central Africa.
Cubans of Asian origin represent 1% of the population. They are mostly of Chinese, Japanese, or Korean origin.
Few remains of the Taínos remain, it is said that 1.02% of the Cuban population. Some American Indians from the United States settled in Cuba in the 19th century (notably the Cherokee, Choctaw, and Seminole). There are no exact figures on his current descendants.
The total population in the official census of 1953 was 5,829,029 people. The population of Cuba has very complex origins and intermarriage between the various groups is so general that this rule will apply.
Cuba’s birth rate (9.88 births per thousand inhabitants in 2006) is one of the lowest in the Western Hemisphere, comparable only to Europe. Its total population has continuously increased from around 7 million in 1961 to more than 11 million now, but the growth rate has stopped in recent decades and has recently declined, the Cuban government confirmed in 2006 the first decrease in the population since the Mariel exodus, although in the 2007-2009 triennium a slight increase of 0.58 per 1000 people was reported. Immigration and emigration have had notable effects on the demographic profile of Cuba during the 20th century. Between 1900 and 1930, about a million Spaniards arrived from Spain.
After the 1959 Revolution, more than a million Cubans left the island, mainly to Miami, Florida, where there is an important community with great political power. The emigration that occurred in the immediate aftermath of the Cuban Revolution was primarily from the predominantly white upper and middle classes, thus contributing to a demographic shift, along with changes in birth rates and racial identifications among various ethnic groups.
DIASPORA
The United States is home to the largest number of Cubans outside of Cuba (almost 1,144,024 in 2010), mostly in Miami and other major Florida cities, as well as in New Jersey, California, New York, Texas, and Puerto Rico. Also in North America live 22,604 Cubans in Mexico and 21,440 in Canada.
Smaller communities of Cubans live in Europe, where Spain with 128,641 Cubans, Italy with 17,947, and Germany with 10,083 have the largest populations. In South America, the largest Cuban communities are in Venezuela with 20,991 and Chile with 3,163. Cubans are spread across the 5 continents.
After the founding of the republic in 1902, considerable migration came from the Iberian Peninsula to the island, including some former Spanish soldiers who had participated in the wars of independence, and yet this was never an obstacle to respect and respect. affection from Cubans, who have always been proud of their Hispanic origins.
CULTURE.
Cuban culture reflects the influences on the island of several different cultures, mainly European (Spanish) and African. This is evident in the idiosyncrasy, in the direct and dynamic but open and witty humor of most Cubans. However, during the period of the republic (1901-1958) Cuban culture was also strongly influenced by the US This was evident in music, sports, architecture, finance, among others. In some respects, many Cubans saw Cuban culture more closely related to the United States than to Mexico or other neighboring Latin American nations. During the revolutionary period (1959 – present) the Soviet influence is present in all planes of daily life, the greatest contributions were in the field of architecture and agriculture. There was a significant migration of Russians, Ukrainians, and Germans, most of them military, to the country, most of them returned to their countries of origin after the collapse of communism in Eastern Europe.
SYMBOLS.
The Cuban flag is red, white, and blue in color and was adopted for the first time by Narciso López in a proposal made by the poet Miguel Teurbe Tolón. The design incorporates three blue stripes, representing the sea that surrounds the island of Cuba and the three departments into which the colony was divided (Occidente, Centro, and Oriente), and two white stripes that symbolize the purity of the patriotic cause. The red triangle represents the bloodshed to liberate the nation. The white star in the triangle represents independence. The shield is an ogival shield, divided into three quarters that represent the Cuban fields, the flag, and the strategic importance of Cuba as a key to the new world or the Gulf of Mexico. The Himno de Bayamo or La Bayamesa is the national patriotic anthem.
 LOS CUBANOS: COMPOSICION RACIAL, DIASPORA, CULTURA Y SIMBOLOS.
LOS CUBANOS: COMPOSICION RACIAL, DIASPORA, CULTURA Y SIMBOLOS.
Los cubanos son las personas originarias de Cuba. La mayoría de los cubanos viven en Cuba (11 193 470) en 2019, aunque también hay una gran diáspora cubana, especialmente en los Estados Unidos donde vivían 1 343 960 cubanos en 2018, en España 151 423 (2019), y México 22 604 (2016).
Las provincias con mayor número de habitantes en Cuba (2010) son La Habana (2 135 498), Santiago de Cuba (1 047 963), Holguín (1 037 573), Granma (836 366), Villa Clara (800 335), y Camagüey (780 598). Según la Oficina Nacional de Estadísticas (ONE) al término de 31 de diciembre de 2010, la población era de 11 241 1616 (5 628 996 hombres y 5 612 165 mujeres).
COMPOSICION RACIAL.
La composición racial en Cuba era en 2002 de 7 271 926 blancos, con los negros y mulatos siendo 1 126 894 y 2 658 675 respectivamente. La población china en Cuba desciende en su mayoría de trabajadores contratados que llegaron en el siglo XIX para construir los ferrocarriles y trabajar en las minas. Después de la Revolución Industrial, muchos de estos trabajadores se quedaron en Cuba porque no podían pagar el pasaje de vuelta a China.
La ascendencia de los cubanos blancos (65,05 %) proviene principalmente de los españoles. Durante los siglos XVIII, XIX y primera parte del siglo XX, especialmente, grandes olas de canarios, gallegos, asturianos y catalanes emigraron de España a Cuba. Otras nacionalidades europeas que inmigraron incluyen: británicos —entre ellos los escoceses—, rusos, polacos, portugueses, rumanos, italianos, griegos, franceses, alemanes e irlandeses. Hay un pequeño remanente de una comunidad judía. También hay una significativa afluencia étnica de diversos pueblos de Oriente Medio, especialmente libaneses, palestinos, turcos y sirios.
Los afro-cubanos componen 10,08 % al 23,84 % de la población. Sus orígenes son principalmente congo, un pueblo de África Central.
Los cubanos de origen asiático representan el 1 % de la población. En su mayoría son de origen chino, japonés o coreano.
De los taínos quedan pocos restos, se dice que el 1,02 % de la población cubana. Algunos indios americanos de los Estados Unidos se establecieron en Cuba en el siglo XIX (en particular, Cherokee, Choctaw y Seminole). No hay cifras exactas sobre sus descendientes actuales.
La población total en el censo oficial de 1953 era 5 829 029 personas. La población de Cuba tiene orígenes muy complejos y los matrimonios mixtos entre los diversos grupos es tan general que se aplicará esta norma.
La tasa de natalidad de Cuba (9,88 nacimientos por cada mil habitantes en 2006) es una de las más bajas del hemisferio occidental, comparable solo con Europa. Su población total ha aumentado continuamente pasando de alrededor de 7 millones en 1961 a más de 11 millones ahora, pero la tasa de crecimiento se ha detenido en las últimas décadas, y ha pasado recientemente a una disminución, el gobierno cubano confirmó en 2006 el primer descenso en la población desde el éxodo del Mariel, aunque en el trienio 2007-2009 se reportó un ligero aumento de 0,58 por 1000 personas. La inmigración y la emigración han tenido notables efectos sobre el perfil demográfico de Cuba durante el siglo XX. Entre 1900 y 1930, cerca de un millón de españoles arribaron desde España.
Después de la Revolución de 1959, más de un millón de cubanos abandonaron la isla, principalmente hacia Miami, Florida, donde existe una importante comunidad con gran poder político. La emigración que se produjo inmediatamente después de la Revolución Cubana era sobre todo de las clases altas y medias predominantemente blancos, contribuyendo así a un cambio demográfico, junto con cambios en las tasas de nacimiento e identificaciones raciales entre los diversos grupos étnicos.
DIASPORA
Los Estados Unidos es el hogar del mayor número de cubanos fuera de Cuba (casi 1 144 024 en 2010), sobre todo en Miami y otras ciudades importantes de Florida, así como en Nueva Jersey, California, Nueva York, Texas y Puerto Rico, también en Norteamérica viven 22 604 cubanos en México y 21 440 en Canadá.
Comunidades más pequeñas de cubanos viven en Europa, donde España con 128 641 cubanos, Italia con 17 947 y Alemania con 10 083 tienen las mayores poblaciones. En América del Sur las mayores comunidades cubanas están en Venezuela con 20 991 y Chile con 3163 Los cubanos están diseminados por los 5 continentes.
Después de la fundación de la república en 1902, una considerable migración llegó desde la península ibérica a la isla, entre ellos algunos exsoldados españoles que habían participado en las guerras de independencia, y sin embargo, esto nunca fue un obstáculo para el respeto y el afecto de los cubanos, que siempre han estado orgullosos de sus orígenes hispanos.
CULTURA.
La cultura cubana refleja las influencias sobre la isla de varias culturas diferentes, principalmente europeos (españoles) y africanos. Esto es evidente en la idiosincrasia, en el humor directo y dinámico pero abierto e ingenioso de la mayoría de los cubanos. Sin embargo, durante el período de la república (1901-1958) la cultura cubana también fue fuertemente influenciada por los EE. UU. Esto fue evidente en la música, deportes, arquitectura, finanzas, entre otros. En algunos aspectos muchos cubanos vieron la cultura cubana más estrechamente relacionada con los Estados Unidos que con México o de otras naciones vecinas de América Latina. Durante el período revolucionario (1959 – actual) la influencia soviética se hace presente en todos los planos de la vida diaria, los mayores aportes fueron en el campo de la arquitectura y la agricultura. Existió una migración importante de rusos, ucranianos y alemanes, la mayoría militares, al país, la mayoría volvieron a sus países de origen luego del colapso del comunismo en Europa del Este.
SIMBOLOS.
La bandera cubana es de color rojo, blanco y azul y fue adoptada por primera vez por Narciso López en una propuesta formulada por el poeta Miguel Teurbe Tolón. El diseño incorpora tres franjas azules, lo que representa el mar que rodea la isla de Cuba y los tres departamentos en que estaba dividida la colonia (Occidente, Centro y Oriente), y dos franjas blancas que simbolizan la pureza de la causa patriótica. El triángulo rojo representa la sangre derramada para liberar a la nación. La estrella blanca en el triángulo representa la independencia. El escudo es una adarga ojival, dividido en tres cuarteles que representan, los campos cubanos, la bandera y la importancia estratégica de Cuba como llave del nuevo mundo o del golfo de México. El Himno de Bayamo o La Bayamesa es el himno patriótico nacional.
Agencies/ Wiki/ Various/ Internet Photos/ Arnoldo Varona/ www.TheCubanHistory.com
THE CUBAN HISTORY, HOLLYWOOD.


 THE CUBANS: Racial Composition, Diaspora, Culture, and Symbols. * LOS CUBANOS: Composición Racial, Diaspora, Cultura y Simbolos Nacionales. PHOTOS.
THE CUBANS: Racial Composition, Diaspora, Culture, and Symbols. * LOS CUBANOS: Composición Racial, Diaspora, Cultura y Simbolos Nacionales. PHOTOS.