CUBA WILL LOSE UP TO 5,000 KILOMETERS OF ITS TERRITORY DURING THIS CENTURY.
The Caribbean Sea penetrates the southern coast of Cuba at a rate of 1.3 meters annually because of climate change, officials from the Ministry of Science and Technology (CITMA) quoted by EFE warned Monday.
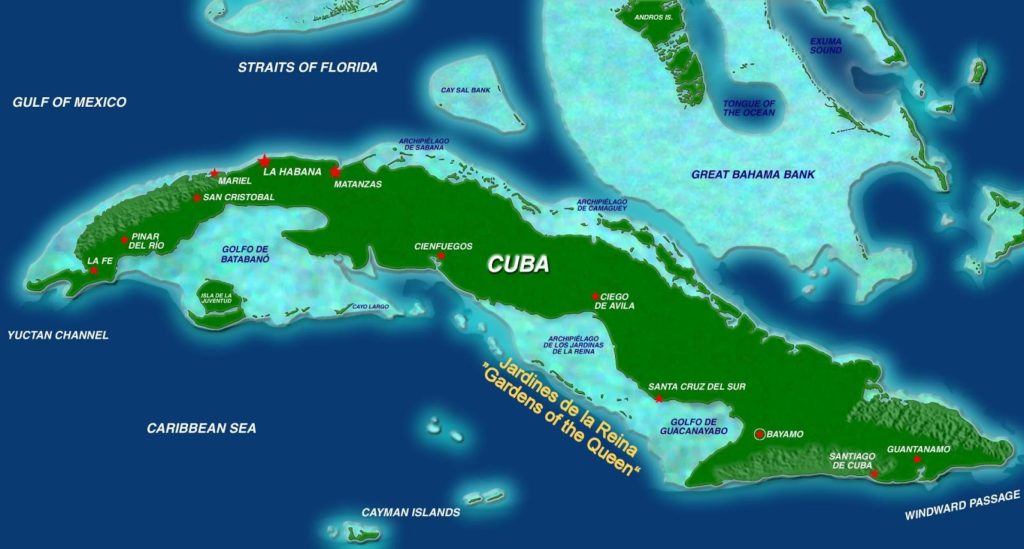
The impact can already be seen in the municipalities of the southern center, La Sierpe and Sancti Spíritus, where saline intrusion, soil erosion and the disappearance of mangroves are observed.
In addition, official reports indicate that sea level has risen rapidly in the last five years and is estimated to rise to about six centimeters per year on the island.
According to calculations by specialists, for the period between 2050 and 2100 the map of Cuba (with a total area of 109,884 square kilometers) will have lost between 2,500 and 5,000 square kilometers.
Climate change affects beaches, tourism development and agricultural production in the province of Sancti Spíritus, due to the rise of the sea, said the CITMA delegate in that territory, Leonel Diaz, quoted by the official agency Prensa Latina.
Currently the companies dedicated to rice cultivation in Sancti Spíritus seek to obtain “varieties that are more resistant to salinity and water stress,” said Díaz.
The penetration of the Caribbean Sea is the main environmental problem derived from climate change that impacts Cuba because of its island condition, according to the report.
In order to face the challenges of climate change, the Cuban government created the “Life Task” project last April, which aims to carry out five strategic actions and 11 tasks aimed at confronting and adapting to the environmental challenges to minimize their effects on Areas.
This state plan says it will focus on 73 municipalities, 63 coastal and 10 non-coastal settlements, and its actions aim at the comprehensive recovery in the short term of 35 sandy beaches for tourist use and coastal protection by 2020 and another 56 by 2050 .
This plan is expected to reduce vulnerability in 15 priority areas, including the areas of Sancti Spíritus and La Sierpe.
Among the Cuban territories most vulnerable to the effects of climate change are those located south of the provinces of Artemisa and Mayabeque, the northern coast of Havana and its bay, Varadero and its tourist corridors, and the keys of Villa Clara, Ciego Of Avila and Camagüey.
CUBA PERDERÁ HASTA 5,000 KILÓMETROS DE SU TERRITORIO DURANTE ESTE SIGLO.
El mar Caribe penetra por la costa sur de Cuba a razón de 1,3 metros anualmente a causa del cambio climático, advirtieron este lunes autoridades del Ministerio de Ciencia Tecnología y Medio Ambiente (CITMA) citadas por EFE.
El impacto ya se aprecia en los municipios del centro sur, La Sierpe y Sancti Spíritus, donde se observan la intrusión salina, la erosión de los suelos y la desaparición de manglares.
Además, informes oficiales indican que el nivel del mar ha subido de forma acelerada en los últimos cinco años y se estima que su elevación alcance unos seis centímetros por año en la Isla.
De acuerdo con cálculos de especialistas, para el periodo comprendido entre los años 2050 y 2100 el mapa de Cuba (con una superficie total de 109.884 kilómetros cuadrados) habrá perdido entre 2.500 y 5.000 kilómetros cuadrados.
El cambio climático afecta a las playas, el desarrollo turístico y la producción agrícola en la provincia de Sancti Spíritus, debido a la elevación del mar, explicó el delegado del CITMA en ese territorio, Leonel Díaz, citado por la agencia oficial Prensa Latina.
Actualmente las empresas dedicadas al cultivo de arroz en Sancti Spíritus buscan obtener “variedades más resistentes a la salinidad y al estrés hídrico”, refirió Díaz.
La penetración del mar Caribe constituye el principal problema ambiental derivado del cambio climático que impacta a Cuba por su condición insular, precisa el reporte.
Con el fin de enfrentar los retos que impone el cambio climático, el Gobierno cubano creó en abril pasado el proyecto “Tarea Vida” que pretende realizar cinco acciones estratégicas y 11 tareas encaminadas al enfrentamiento y adaptación a los retos medioambientales para minimizar sus efectos en las zonas vulnerables.
Ese plan estatal dice que se concentrará en 73 municipios, 63 asentamientos costeros y diez no costeros, y sus acciones se proponen la recuperación integral a corto plazo de 35 playas arenosas de uso turístico y protección costera para el año 2020 y otras 56 hacia el 2050.
Dentro de ese plan se prevé disminuir la vulnerabilidad en 15 zonas prioritarias, entre ellas las áreas de Sancti Spíritus y La Sierpe.
Entre los territorios cubanos más vulnerables a los efectos del cambio climático se encuentran los situados al sur de las provincias de Artemisa y Mayabeque, el litoral norte de La Habana y su bahía, Varadero y sus corredores turísticos, y los cayos de Villa Clara, Ciego de Ávila y Camagüey.
Agencies/DDC/ Internet Photos/ Arnoldo Varona/ TheCubanHistory.com
THE CUBAN HISTORY, HOLLYWOOD.